The Living Planet Report 2020 (LPR) shows us that global biodiversity loss is at its worst. In order to give better directions for allocating resources, a regional assessment was performed, which Earth.org distills for you in their article.
In the LPR 2020, five major threat categories were used to illustrate the impacts that are driving biodiversity’s decline. Through this frame, governments and organizations can better come up with solutions or mitigations that are suitable for the ecosystems as well as the local communities.

Soure: Living Planet Report 2020, WWF.
The analysis was carried out for 5 regions: Europe and Central Asia, Asia Pacific, Latin America & Caribbean, Africa and North America. Taking species population as a measure, a significant loss in biodiversity was found in all regions, with encroachment on natural land identified as the most prominent threat to wildlife. Latin America & the Caribbean have sustained a loss of 94% since 1975.
Here, we will guide you through threats each region is facing and give some current examples.
North America
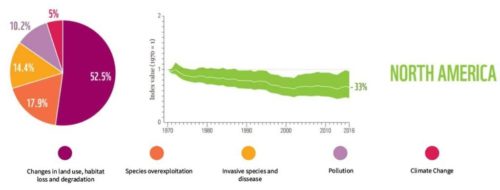
Source: WWF Living Planet Report 2020.
- Nearly 3 billion birds lost in the past 50 years
- Possible causes: Habitat loss, chemical pollution (pesticide)
- Water level of the Great Lakes, biggest freshwater reservoir area in North America, at a historical low
- 30% of its plant-pollination network has disappeared
Europe and Central Asia
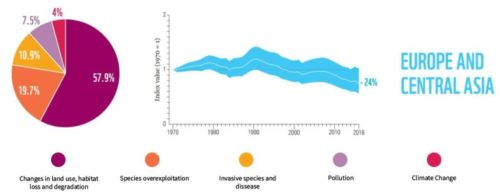
Source: WWF Living Planet Report 2020.
- Only 23% of species and 16% of its habitats are in good health
- 1,677 out of 15,060 European species are threatened with extinction; most endangered are snails, clams and fish
- 6 animal, bird and fish species, including the Saiga antelope, the gyrfalcon and the Persian leopard, are facing risk of extinction in Russia
Latin America & Caribbean
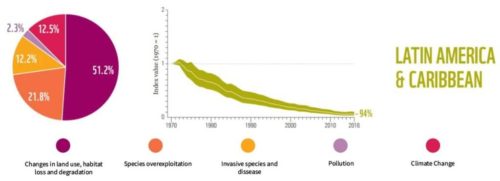
Source: WWF Living Planet Report 2020.
- Major negative trends observed in reptiles, amphibians and fish
- A type of chytrid fungus, which originated in Asia, has been causing declines in 500 amphibian species and driven around 90 of them to extinction
- 2019 record breaking dry seasons and forest fires lead to a surge in deforestation, with 30% more than the previous year
Africa
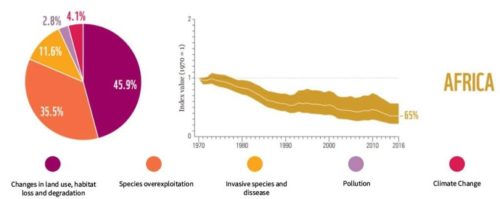
Source: WWF Living Planet Report 2020.
- Increasing threats of extinction for the species in the Mara River Basin
- The ecosystem provides livelihood for around 1.1 million locals
- 76% of endemic freshwater species in Lake Victoria are threatened with extinction
- Illegal hunting and mining have driven down the Grauer’s gorilla population in the Congo by 87%.
Asia Pacific
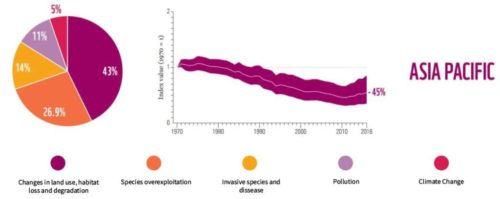
Source: Living Planet Report 2020.
- Nearly 3 billion animals were killed or displaced by Australia’s devastating bushfire season of 2019 and 2020
- In India, 3% of bird species face extinction; 19% of amphibians are threatened or critically endangered; over 12% of wild mammal species are threatened with extinction
- More than 80% of East and Southeast Asia’s wetlands are classified as threatened due to human activity.
We are in a time of global upheaval, both politically, economically and in regards to our environment. The latter has not yet superseded the two former, but report like the LPR are driving a growing understanding on the gravity of the situation. Our life-support system, the world we live in, is in a critical state and to simply understand and acknowledge this is the first step.



